What is GDPR? A Beginner’s Guide to Website Compliance
Discover how to make your website GDPR-compliant with this beginner-friendly guide covering key principles, consent requirements, and essential compliance steps.
In today’s digital landscape, data privacy regulations have become a critical consideration for website owners and businesses across the globe. Among these regulations, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) stands out as one of the most comprehensive and impactful privacy laws. Whether you’re a small business owner, a marketer, or an IT professional, understanding GDPR is essential for operating legally online.
But what exactly is GDPR, and how does it affect your website? This beginner’s guide will walk you through the basics of GDPR compliance, common pitfalls, and practical steps to ensure your website meets the requirements.
What is GDPR?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a comprehensive data protection and privacy regulation implemented by the European Union. It came into effect on May 25, 2018, and represents one of the most significant changes to data privacy regulation in decades.
Definition and Scope: GDPR regulates how organizations must handle personal data of EU residents. Personal data includes any information relating to an identified or identifiable natural person, such as names, identification numbers, location data, online identifiers like IP addresses, or factors specific to the physical, physiological, genetic, mental, economic, cultural, or social identity of that person.
Who Needs to Comply: Contrary to common misconception, GDPR doesn’t just apply to EU-based organizations. It has an extraterritorial scope, meaning it applies to:
- Organizations established within the EU, regardless of where the data processing takes place
- Organizations outside the EU that offer goods or services to EU residents
- Organizations that monitor the behavior of EU residents
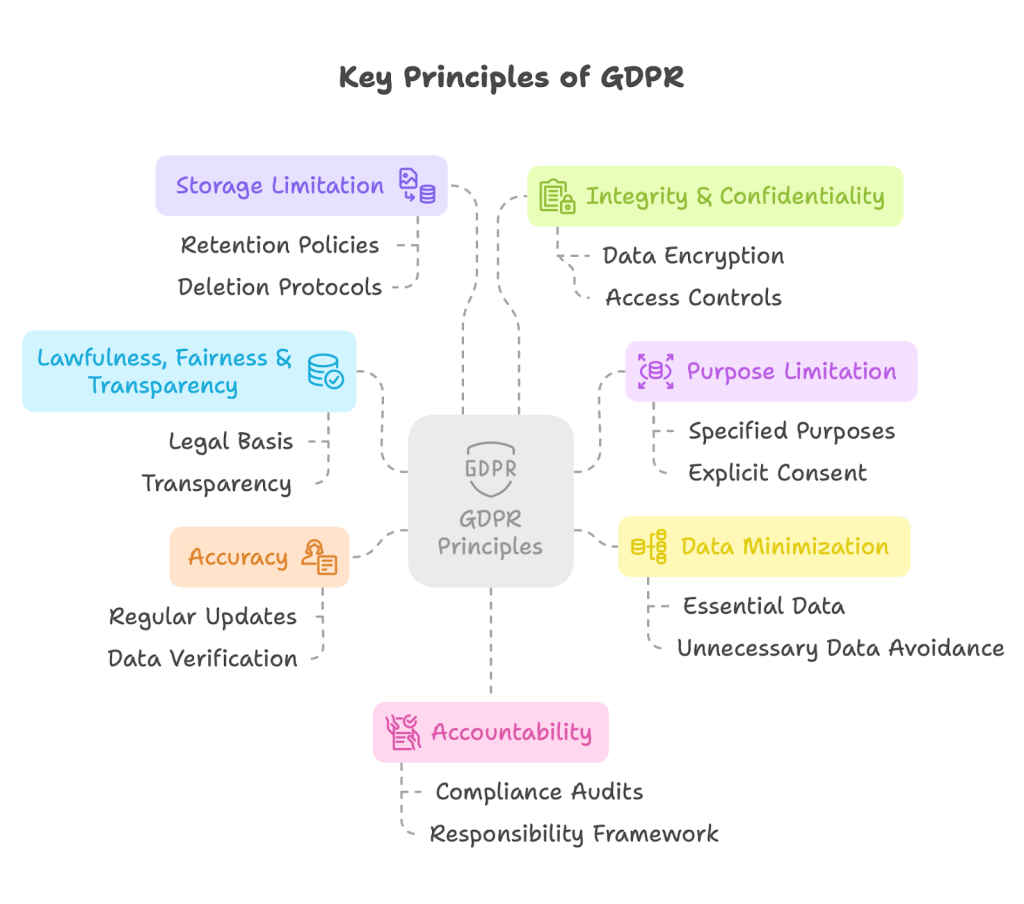
Core Principles of GDPR: GDPR is built on seven key principles that guide how personal data should be handled:
- Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency
- Purpose limitation
- Data minimization
- Accuracy
- Storage limitation
- Integrity and confidentiality (security)
- Accountability
Understanding these principles is the first step toward ensuring your website’s compliance with GDPR.
Key Requirements for Website Compliance
For websites to be GDPR compliant, they must meet several specific requirements that protect user data at every touchpoint. Here are the essential elements you need to address:
Lawful Basis for Processing
Under GDPR, you need a legal basis to process personal data. The six lawful bases are:
- Consent: The individual has given clear consent for you to process their personal data for a specific purpose.
- Contract: The processing is necessary for a contract you have with the individual.
- Legal obligation: The processing is necessary for you to comply with the law.
- Vital interests: The processing is necessary to protect someone’s life.
- Public task: The processing is necessary for you to perform a task in the public interest.
- Legitimate interests: The processing is necessary for your legitimate interests or the legitimate interests of a third party.
For most websites, consent and legitimate interests are the most commonly used bases for processing.
Consent Requirements
When relying on consent, GDPR sets a high standard for what qualifies as valid consent:
- It must be freely given, specific, informed, and unambiguous
- It requires a clear affirmative action (pre-ticked boxes are not allowed)
- It must be as easy to withdraw consent as it is to give it
- Consent requests must be presented clearly and separately from other terms and conditions
This means those ubiquitous cookie banners that only offer an “Accept” button without the option to decline don’t meet GDPR requirements.

Privacy Policies
Your website must have a comprehensive privacy policy that explains:
- What personal data you collect
- Why you collect it
- How you use it
- How long you keep it
- Who you share it with
- How users can exercise their rights regarding their data
The policy should be written in clear, plain language that is easy for the average person to understand.
Data Subject Rights
GDPR grants individuals several rights regarding their personal data, including:
- Right to be informed
- Right of access
- Right to rectification
- Right to erasure
- Right to restrict processing
- Right to data portability
- Right to object
- Rights related to automated decision making and profiling
Your website needs mechanisms in place to handle these requests efficiently.
Common Website Compliance Issues
Despite GDPR being in effect for several years now, many websites still struggle with compliance issues. Let’s explore the most frequent problems:
Third-Party Services Sending Data Outside EU
One of the most prevalent GDPR compliance issues is the transfer of personal data outside the European Economic Area (EEA). This happens frequently through third-party services embedded in websites.
For instance, a German court ruled that embedding Google Fonts directly from Google’s servers violates GDPR because it sends visitors’ IP addresses to servers in the US without proper consent or another valid legal basis.
You can quickly check if your website is sending data outside the EU using our free tool at violating-gdpr.com. Our tool scans your website for elements that might be transferring personal data to non-EU servers.
Cookie Consent Mechanisms
Many websites still use non-compliant cookie consent mechanisms, such as:
- Implied consent (assuming a user consents by continuing to browse)
- Not providing a clear way to reject non-essential cookies
- Pre-ticked consent boxes
- Cookie walls that block access unless consent is given
A compliant cookie banner should:
- Allow users to decline non-essential cookies easily
- Provide granular choices for different types of cookies
- Not load non-essential cookies before consent is obtained
Contact Forms and Data Collection
Contact forms are a common source of personal data collection on websites. To make them GDPR-compliant:
- Only collect necessary information
- Clearly explain how the data will be used
- Get explicit consent before using the data for marketing purposes
- Ensure the data is securely processed and stored
Google Analytics and Other Tracking Tools
Analytics tools collect various types of user data, which can be problematic under GDPR. Some considerations include:
- Configuring analytics tools to anonymize IP addresses
- Obtaining proper consent before enabling tracking
- Ensuring data processing agreements are in place with providers
- Using EU-based alternatives where possible
Embedded Content
Embedded content from third-party platforms like YouTube, Google Maps, or social media can also transfer personal data outside the EU. Solutions include:
- Using local copies of resources (e.g., hosting Google Fonts on your own server)
- Implementing two-click solutions that only load external content after user consent
- Using privacy-friendly alternatives (e.g., self-hosted video players)
Steps to Achieve GDPR Compliance
Achieving GDPR compliance requires a systematic approach to evaluating and improving your website’s data practices. Follow these key steps:
Conduct a Data Audit
Start by understanding what personal data your website collects, processes, and stores. This includes:
- User account information
- Contact form submissions
- Newsletter subscriptions
- IP addresses and cookies
- Analytics data
- Third-party integrations that may collect data
A thorough data audit will help you identify potential compliance issues.
Update Privacy Policies
Ensure your privacy policy is clear, comprehensive, and accessible. It should:
- Be written in plain language
- Explain all data processing activities
- Outline how users can exercise their rights
- Be easily accessible from any page on your website
Implement Proper Consent Mechanisms
Review and update your consent mechanisms to ensure they meet GDPR requirements:
- Make them transparent and user-friendly
- Allow users to give or withhold consent for different purposes
- Document and store consent
- Make it easy for users to withdraw consent
Review Third-Party Services
Evaluate all third-party services your website uses:
- Check where they process and store data
- Verify they have appropriate data processing agreements
- Consider alternatives if they don’t comply with GDPR
Our tool at violating-gdpr.com can help identify third-party services on your website that might be sending data outside the EU, which is a key step in this review process.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Understanding the potential repercussions of non-compliance can help prioritize your GDPR implementation efforts. Here are the main risks:
Potential Fines and Penalties
GDPR violations can lead to significant financial penalties:
- Up to €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover (whichever is higher) for serious infringements
- Up to €10 million or 2% of annual global turnover for less severe violations
Reputation Damage
Beyond financial penalties, GDPR violations can damage your reputation and erode customer trust. In an era where data privacy concerns are growing, demonstrating a commitment to protecting user data can be a competitive advantage.
Recent Court Cases
Several recent court decisions have highlighted the importance of GDPR compliance:
- In January 2022, a German court ruled that a website using Google Fonts violated GDPR by transferring a user’s IP address to Google’s servers without consent.
- The Austrian Data Protection Authority found that using Google Analytics violated GDPR due to data transfers to the US.
- In 2020, the Court of Justice of the European Union invalidated the Privacy Shield framework, complicating legal data transfers to the US.
These cases emphasize that even seemingly minor compliance issues can have significant consequences.
Tools and Resources for GDPR Compliance
Fortunately, a range of tools and resources are available to help you navigate the complexities of GDPR compliance:
GDPR Compliance Checking Tool
At violating-gdpr.com, we offer a free tool that checks if your website is sending data outside the EU. Our tool:
- Scans your website for external resources like scripts, images, videos, and iframes
- Identifies where these resources are hosted
- Alerts you to potential GDPR compliance issues
This initial check can help you identify areas that need attention before they become compliance problems.
Other Helpful Resources
- The official European Commission GDPR portal
- Your country’s data protection authority website
- Privacy-focused WordPress plugins for website owners
- GDPR compliance checklist templates
Conclusion
GDPR compliance isn’t a one-time task but an ongoing commitment to protecting user data. As website technologies evolve and legal interpretations of GDPR develop through court cases, staying informed and adaptable is essential.
Start by conducting a thorough assessment of your website’s data collection practices, then implement the necessary changes to achieve compliance. Remember that demonstrating a commitment to data privacy isn’t just about avoiding penalties—it’s about building trust with your users.
Take the first step toward GDPR compliance today by using our free checking tool at violating-gdpr.com to see if your website is potentially violating GDPR by sending data outside the EU. Understanding your current compliance status is the foundation for building a more privacy-respecting website.
