Why GDPR Matters: Understanding the Risks of Non-Compliance
Uncover the significant financial, legal, and reputational risks of GDPR non-compliance—and learn how to safeguard your business from costly data privacy pitfalls.
In today’s digital landscape, data has become the lifeblood of businesses. From customer information to employee records, organizations collect, process, and store vast amounts of personal data every day. However, with this power comes great responsibility – especially when it comes to the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Since its implementation in May 2018, GDPR has fundamentally changed how businesses handle personal data of European Union citizens. Yet, despite being in effect for several years, many organizations still struggle with compliance, often unknowingly putting themselves at significant risk.
This comprehensive guide explores why GDPR compliance matters, the substantial risks of non-compliance, and practical steps to protect your organization.
What is GDPR? A Quick Refresher
The General Data Protection Regulation represents the most significant change to European data privacy regulation in decades. Designed to harmonize data privacy laws across Europe, GDPR aims to protect EU citizens’ data privacy and reshape how organizations approach data privacy.
GDPR is built on seven key principles:
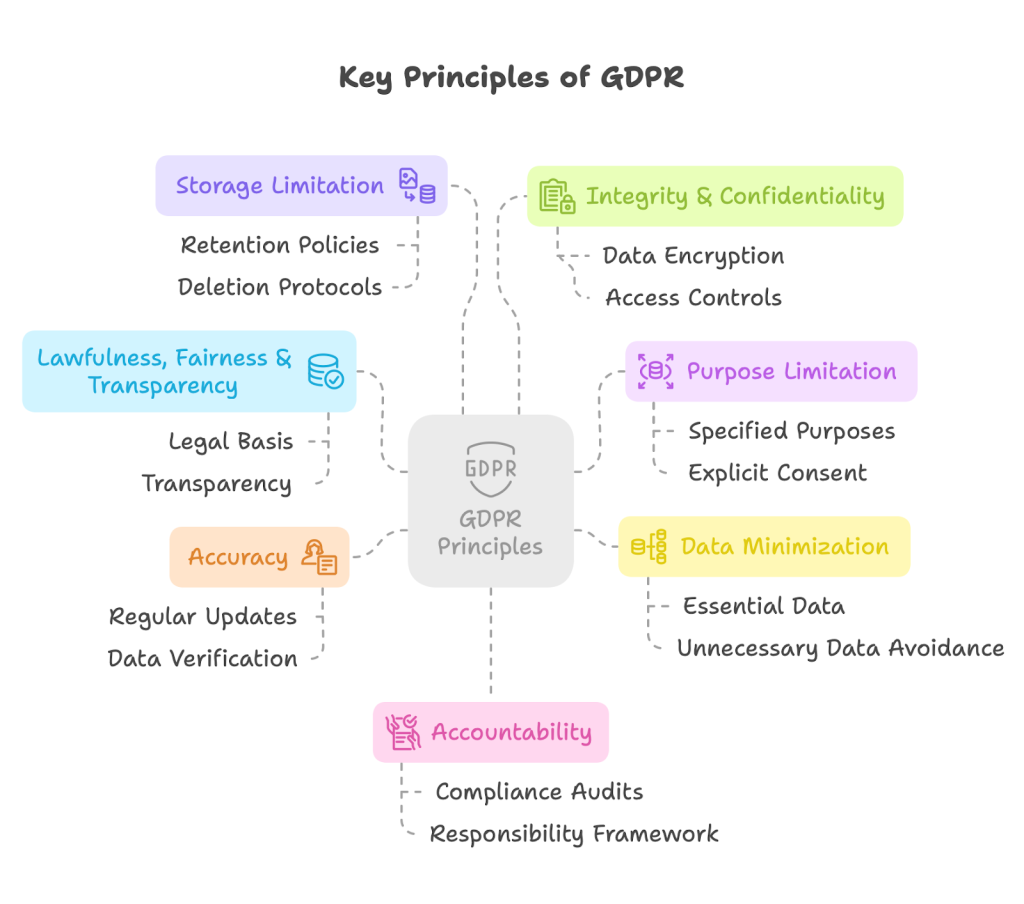
- Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency in data processing
- Purpose limitation (collecting data for specified, explicit purposes)
- Data minimization (collecting only what’s necessary)
- Accuracy of personal data
- Storage limitation (keeping data only as long as needed)
- Integrity and confidentiality (security)
- Accountability (taking responsibility for compliance)
Any organization that processes personal data of EU residents must comply with GDPR – regardless of where the organization is based. This extraterritorial reach makes GDPR relevant for businesses worldwide.
The Real Costs of Non-Compliance
When organizations fail to comply with GDPR, the consequences can be severe and far-reaching.
Financial Penalties
GDPR violations can result in substantial fines. There are two tiers:
- Lower tier: Up to €10 million or 2% of global annual revenue, whichever is higher
- Upper tier: Up to €20 million or 4% of global annual revenue, whichever is higher
These aren’t just theoretical numbers. Major companies have faced significant penalties:
- Google was fined €50 million by French authorities for lack of transparency and inadequate consent mechanisms (source)
- H&M received a €35.3 million fine for excessive employee surveillance (source)
- British Airways was hit with a €20 million penalty following a data breach affecting 400,000 customers (source)
Legal Consequences
Beyond fines, non-compliance can trigger legal actions:
- Data protection authorities may issue orders to cease processing
- Affected individuals can file claims for compensation
- Class-action lawsuits can amplify financial exposure
Business Disruption
GDPR investigations themselves can be highly disruptive. Organizations often need to:
- Redirect resources to address immediate compliance issues
- Halt certain data processing activities
- Deal with lengthy document requests and audits
Recent court rulings have further complicated compliance requirements. For instance, a German court ruled that embedding Google Fonts violates GDPR because it sends IP addresses to the US without proper consent. Similarly, Austrian and French courts have determined that transferring IP information outside the EU can breach GDPR regulations when combined with other data points.
These rulings highlight how seemingly innocuous website elements – like fonts or third-party scripts – can create compliance issues. Simple checks, like using a GDPR compliance tool, can help identify these potential violations before they become problems.
Beyond Fines: The Hidden Risks of GDPR Violations
Financial penalties often grab headlines, but non-compliance risks extend far beyond monetary costs.
Reputation Damage and Loss of Trust
In an era where privacy concerns are at an all-time high, GDPR violations can severely damage brand reputation. Studies show that 81% of consumers would stop engaging with a brand following a data breach or privacy violation.
Once trust is lost, it’s extraordinarily difficult to rebuild – particularly in industries where data security is paramount, such as healthcare, finance, and e-commerce.
Competitive Disadvantage
GDPR compliance can actually become a competitive advantage. Organizations that demonstrate strong data protection practices often win customer preference over those with questionable privacy practices.
Conversely, non-compliant organizations may find themselves losing business to competitors who emphasize their commitment to data protection.
Loss of Business Partnerships
Many businesses now require GDPR compliance from their vendors and partners. Non-compliance can lead to:
- Exclusion from tender processes
- Termination of existing contracts
- Inability to form new business relationships
This “compliance ripple effect” means that even if your organization doesn’t directly serve EU customers, your business relationships might still require GDPR compliance.
Internal Organizational Impacts
GDPR violations can also cause significant internal disruption:
- Staff morale may suffer if the organization is publicly criticized
- Time and resources are diverted from core business activities
- Leadership may face personal accountability
Using specialized tools like the Violating GDPR checker can help organizations quickly identify if their websites might be sending data outside the EU – one of the common compliance issues that organizations face but might not be aware of.
Common GDPR Compliance Mistakes
Understanding typical compliance pitfalls can help organizations avoid them.
Inadequate Consent Mechanisms
Many organizations fail to obtain proper consent for data processing. Common mistakes include:
- Pre-ticked consent boxes (which are explicitly prohibited)
- Vague or overly broad consent requests
- Failure to provide easy withdrawal options for consent
- Bundling consent for different data processing activities
Improper Data Transfer Outside EU
Transferring personal data outside the European Economic Area requires specific safeguards. Problems often arise when:
- Websites embed third-party resources from non-EU servers
- Cloud services store data in non-EU regions
- International data sharing lacks proper data transfer agreements
This is where tools like our GDPR compliance checker become invaluable. By scanning your website for elements that might transfer data outside the EU (like embedded videos, scripts, iframes, and images), it provides an initial assessment of potential compliance issues that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Poor Documentation
GDPR requires organizations to document their data processing activities and compliance measures. Common documentation failures include:
- Incomplete records of processing activities
- Missing data protection impact assessments
- Inadequate documentation of consent
- Poor breach response procedures
Incomplete Privacy Policies
Privacy policies must be clear, comprehensive, and accessible. Many organizations have policies that:
- Use overly complex language
- Fail to specify all data processing purposes
- Don’t adequately explain data subject rights
- Lack information on international transfers
Failing to Respect Data Subject Rights
GDPR grants individuals specific rights regarding their personal data. Organizations often struggle to implement processes for handling:
- Subject access requests
- Right to erasure (“right to be forgotten”)
- Data portability requests
- Objections to processing
How to Ensure GDPR Compliance
Achieving GDPR compliance requires a systematic approach:
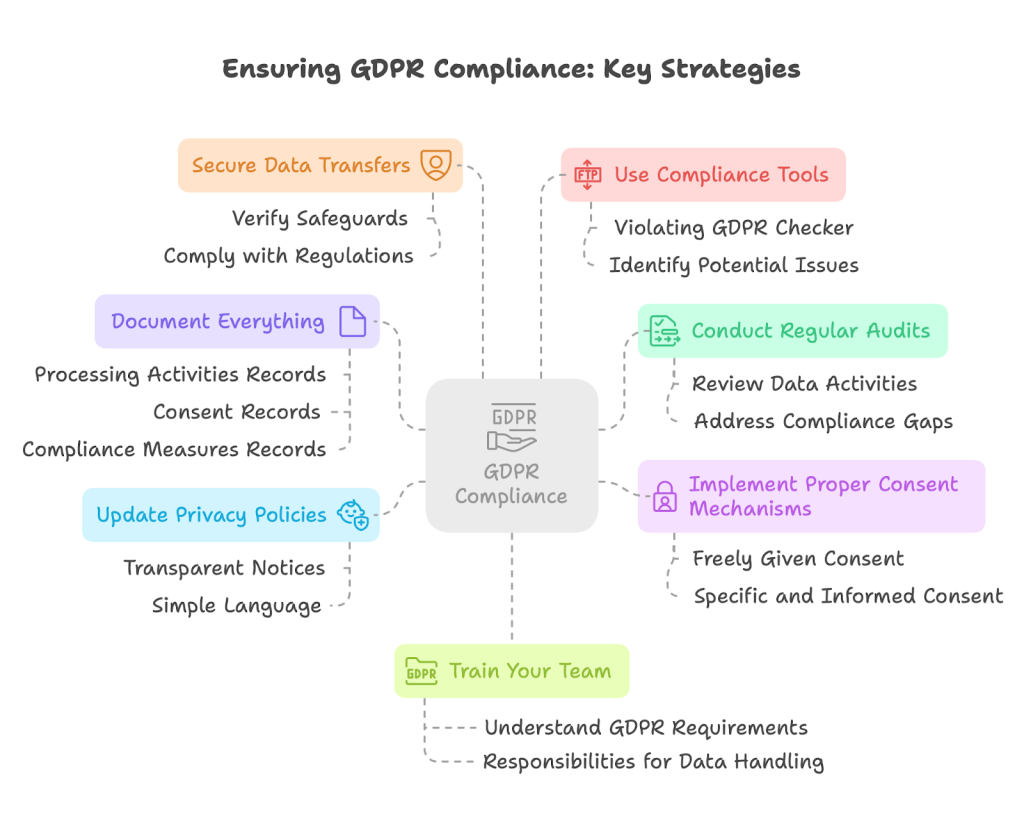
Data Protection Impact Assessments
For high-risk processing activities, organizations should conduct Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) to:
- Identify potential privacy risks
- Assess the necessity and proportionality of processing
- Implement measures to mitigate risks
- Document the assessment process and outcomes
Regular Compliance Audits
Regular audits help ensure ongoing compliance:
- Review data processing activities
- Verify consent mechanisms
- Check third-party data processors
- Evaluate technical security measures
An easy first step is to use tools like our free GDPR compliance checker. It quickly scans your website to identify if you’re sending data outside the EU – one of the key areas where organizations unknowingly violate GDPR regulations.
Staff Training
Employees are often the weakest link in data protection. Effective training should:
- Explain GDPR principles and requirements
- Cover practical scenarios relevant to specific roles
- Address data breach response procedures
- Be regularly updated and refreshed
Working with Experts
For many organizations, working with GDPR specialists is the most efficient path to compliance:
- Data Protection Officers (either internal or external)
- Privacy consultants
- Legal advisors with GDPR expertise
- Technical experts for implementation
Using Compliance Tools
Technology can streamline compliance efforts:
- Privacy management platforms
- Consent management tools
- Data mapping solutions
- Compliance scanning tools like our GDPR violation checker
The Future of Data Protection Regulations
GDPR represents a watershed moment in privacy regulation, but it’s just the beginning.
Evolution of GDPR Enforcement
We’re seeing:
- Increasingly aggressive enforcement
- Focus on specific industries (technology, healthcare, finance)
- Greater emphasis on technical measures
- More coordination between national authorities
Similar Regulations Worldwide
GDPR has inspired similar legislation globally:
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
- Brazil’s General Data Protection Law (LGPD)
- India’s Personal Data Protection Bill
- China’s Personal Information Protection Law
This global trend toward stricter privacy regulation means organizations should view GDPR compliance as part of a broader privacy strategy.
Preparing for Stricter Implementation
Forward-thinking organizations are:
- Implementing privacy by design principles
- Building flexible compliance frameworks
- Staying informed about regulatory developments
- Treating data protection as an ongoing commitment
Protecting Your Business Through Compliance
GDPR compliance shouldn’t be viewed merely as a legal obligation but as a business imperative. The risks of non-compliance – from substantial fines to reputational damage – far outweigh the costs of implementing proper data protection measures.
Organizations that embrace GDPR principles often discover unexpected benefits: improved data management, enhanced customer trust, and better business processes. In contrast, those that treat compliance as an afterthought face increasing risks in an environment of stricter enforcement and growing privacy awareness.
Don’t wait for a violation to take GDPR seriously. Take the first step today by checking if your website might be violating GDPR by sending data outside the EU. Our free tool at violating-gdpr.com provides a quick initial assessment that could help you identify potential issues before they become costly problems.
Remember, when it comes to GDPR compliance, an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure.
