How to Make Your Website GDPR-Compliant: Key Changes to Implement
Implement key technical changes—like self-hosting fonts and auditing cookies—to ensure your website aligns with GDPR requirements and avoids costly compliance pitfalls.
In today’s digital landscape, data privacy isn’t just a legal requirement—it’s a fundamental expectation from your users. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has transformed how businesses handle personal data, especially for websites that serve European users.
But here’s the reality: Many businesses still struggle with implementation, often unaware that seemingly innocent practices—like embedding Google Fonts or using certain analytics tools—could lead to significant compliance issues. In fact, recent court rulings across Europe have made it clear that even sending IP addresses outside the EU can constitute a GDPR violation.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the key changes needed to make your website GDPR-compliant, helping you avoid potential penalties while building trust with your audience.
Understanding GDPR: The Basics You Need to Know
Before diving into the technical implementations, let’s establish a clear understanding of what GDPR compliance actually means for your website.
What GDPR Really Means for Your Website
GDPR is the most comprehensive data protection law ever enacted, affecting any organization worldwide that processes personal data of EU residents.
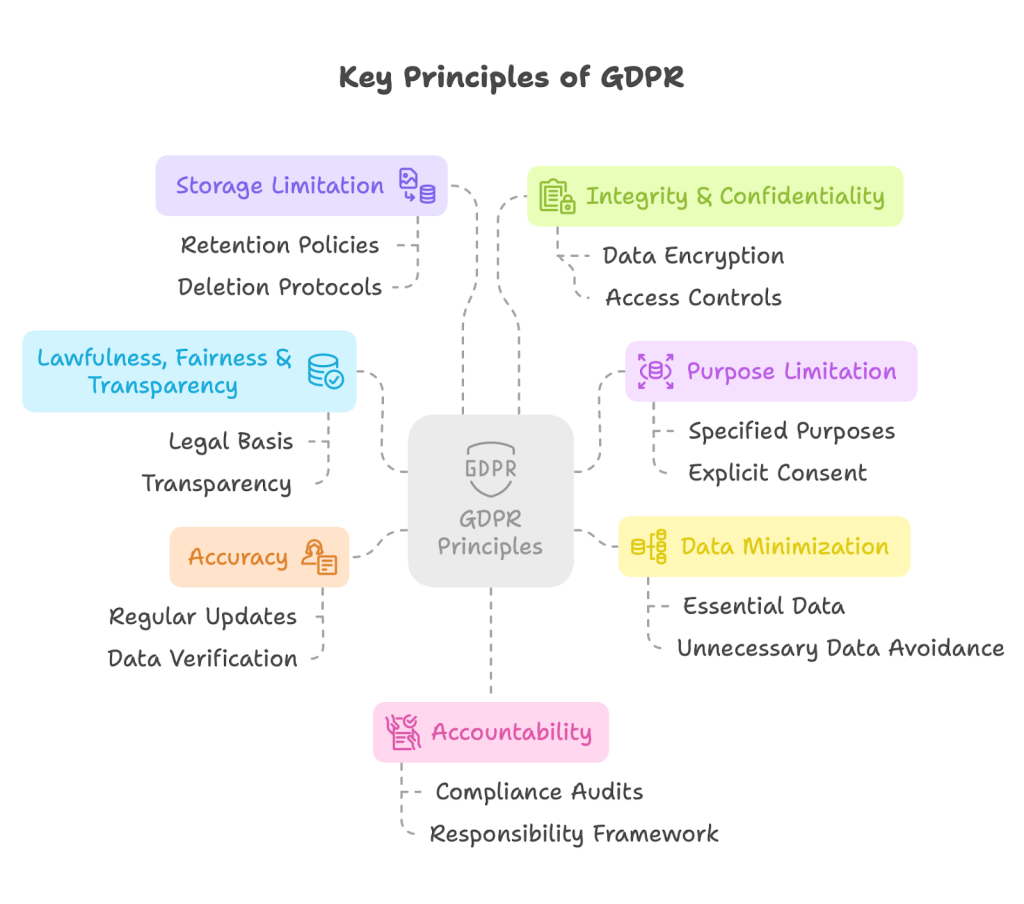
For website owners, this means:
- Being transparent about data collection
- Having a legal basis for processing data
- Implementing appropriate security measures
- Respecting user rights regarding their data
- Ensuring third-party services you use are also compliant
The Real Cost of Non-Compliance
The financial implications of GDPR violations are substantial, with fines reaching up to €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover, whichever is higher. But beyond the monetary penalties, there’s also reputational damage to consider.
Recent rulings highlight how seriously EU courts take these matters. In 2022, a German court ruled that a website embedding Google Fonts directly from Google’s servers violated GDPR because it unnecessarily transmitted visitors’ IP addresses to Google in the U.S. Similarly, Austrian and French courts have ruled against organizations transferring IP addresses outside the EU.
Using a tool like Violating GDPR can quickly identify if your website is unknowingly sending data outside the EU, helping you address potential compliance issues before they become legal problems.
Essential Technical Changes for GDPR Compliance
To ensure your website meets GDPR requirements, you’ll need to implement several technical changes. Here’s what you need to prioritize:
1. Review and Optimize Your Cookie Policy
Cookies are small data files stored in users’ browsers that help websites remember preferences, login details, and browsing behavior. Under GDPR, you must:
Implement Proper Cookie Consent
A compliant cookie banner should:
- Appear before any non-essential cookies are set
- Provide clear information about cookie purposes
- Allow users to accept or reject cookies by category
- Function properly (many cookie banners look compliant but still set tracking cookies regardless of user choice)
Audit Your Existing Cookies
Conduct a comprehensive audit of all cookies on your site and categorize them:
- Essential cookies: Required for basic site functionality
- Preference cookies: Remember user choices
- Statistics cookies: Collect anonymous analytics
- Marketing cookies: Track users across websites for advertising
Only essential cookies can be set without explicit consent. All others require user opt-in.
2. Revise Third-Party Integrations
Third-party services can be a significant source of GDPR violations, especially those transferring data outside the EU.
External Fonts and CDNs
Following the German court ruling on Google Fonts, consider:
- Self-hosting fonts instead of loading them from external CDNs
- Using system fonts that don’t require external loading
- If using CDNs, ensure they have proper GDPR safeguards in place
Analytics Tools
Many popular analytics tools transfer data to servers outside the EU. Consider these alternatives:
- Configure Google Analytics to anonymize IP addresses (though this may not be sufficient under stricter interpretations)
- Use EU-based analytics platforms like Matomo or Plausible
- Consider server-side analytics that doesn’t use cookies
You can quickly check if your site is sending data outside the EU using the Violating GDPR checker tool, which scans for external resources that might be causing compliance issues.
3. Update Your Forms and Data Collection Points
Forms are primary data collection points and require special attention:
Implement Clear Consent Mechanisms
For each form:
- Include clear, specific consent checkboxes that aren’t pre-checked
- Explain exactly what the data will be used for
- Link to your privacy policy
- Make consent as granular as possible (separate consents for different purposes)
Minimize Data Collection
Apply the principle of data minimization:
- Only collect information that’s absolutely necessary
- Remove any fields that gather “nice to have” but non-essential information
- Document your justification for each piece of data collected
4. Create or Update Your Privacy Policy
A comprehensive privacy policy is not just legally required—it’s also an opportunity to build trust with your users.
Essential Components of a GDPR-Compliant Privacy Policy
Your privacy policy should clearly explain:
- What personal data you collect
- Why you collect it (specific purposes)
- The legal basis for processing (consent, legitimate interest, etc.)
- How long you retain data
- Whether data is transferred outside the EU
- Who you share data with
- User rights under GDPR
- How users can contact you regarding their data
Make It Accessible and Understandable
Privacy policies should be:
- Written in clear, plain language
- Easily accessible from every page of your website
- Regularly updated as your data practices change
- Available in all languages your website serves
Implementing User Rights Under GDPR
GDPR grants users specific rights regarding their personal data, which your website must accommodate.
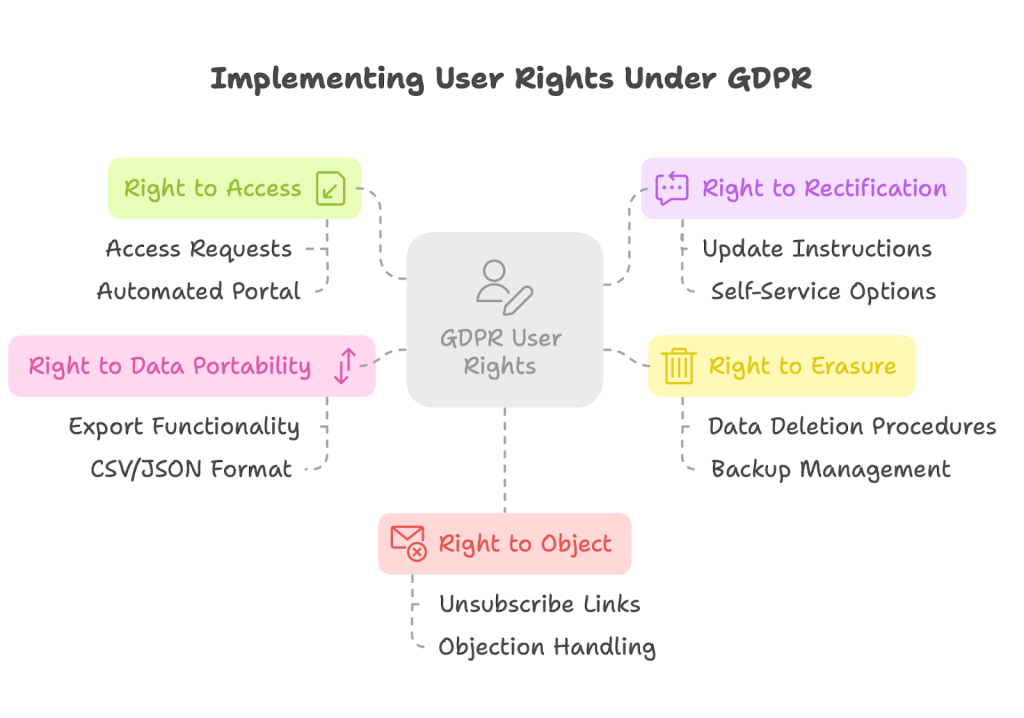
1. Right to Access
Users have the right to know what personal data you have about them and how it’s being used.
Implementation: Create a process for handling data access requests, whether through an automated portal or a manual system managed by your team.
2. Right to Rectification
Users can request corrections to inaccurate personal data.
Implementation: Provide clear instructions on how users can update their information, or set up self-service options where possible.
3. Right to Erasure (Right to Be Forgotten)
Users can request deletion of their personal data under certain circumstances.
Implementation: Develop procedures for identifying and deleting user data across all systems, including backups and third-party services.
4. Right to Data Portability
Users can request their data in a machine-readable format to transfer to another service.
Implementation: Create export functionality that compiles user data in a standard format like CSV or JSON.
5. Right to Object
Users can object to certain types of processing, including direct marketing.
Implementation: Include unsubscribe links in all marketing communications and establish processes for handling objections to other forms of processing.
Beyond Technical Solutions: Creating a Privacy-First Culture
True GDPR compliance extends beyond technical implementations. It requires a privacy-first approach to all aspects of your website operations.
Data Protection by Design and Default
Integrate privacy considerations into every new feature or change to your website:
- Conduct data protection impact assessments for new features
- Default to the most privacy-friendly settings
- Consider privacy implications during the planning stage, not as an afterthought
Staff Training and Awareness
Your team should understand GDPR requirements and how they apply to their roles:
- Conduct regular training sessions
- Develop clear internal policies for handling personal data
- Create procedures for detecting and reporting data breaches
Regular Compliance Audits
GDPR compliance isn’t a one-time effort but requires ongoing attention:
- Schedule regular audits of your website and practices
- Keep documentation up to date
- Stay informed about evolving interpretations and court decisions
Practical Steps to Implement GDPR Compliance
Now that we’ve covered the key requirements, let’s outline a practical roadmap for implementation:
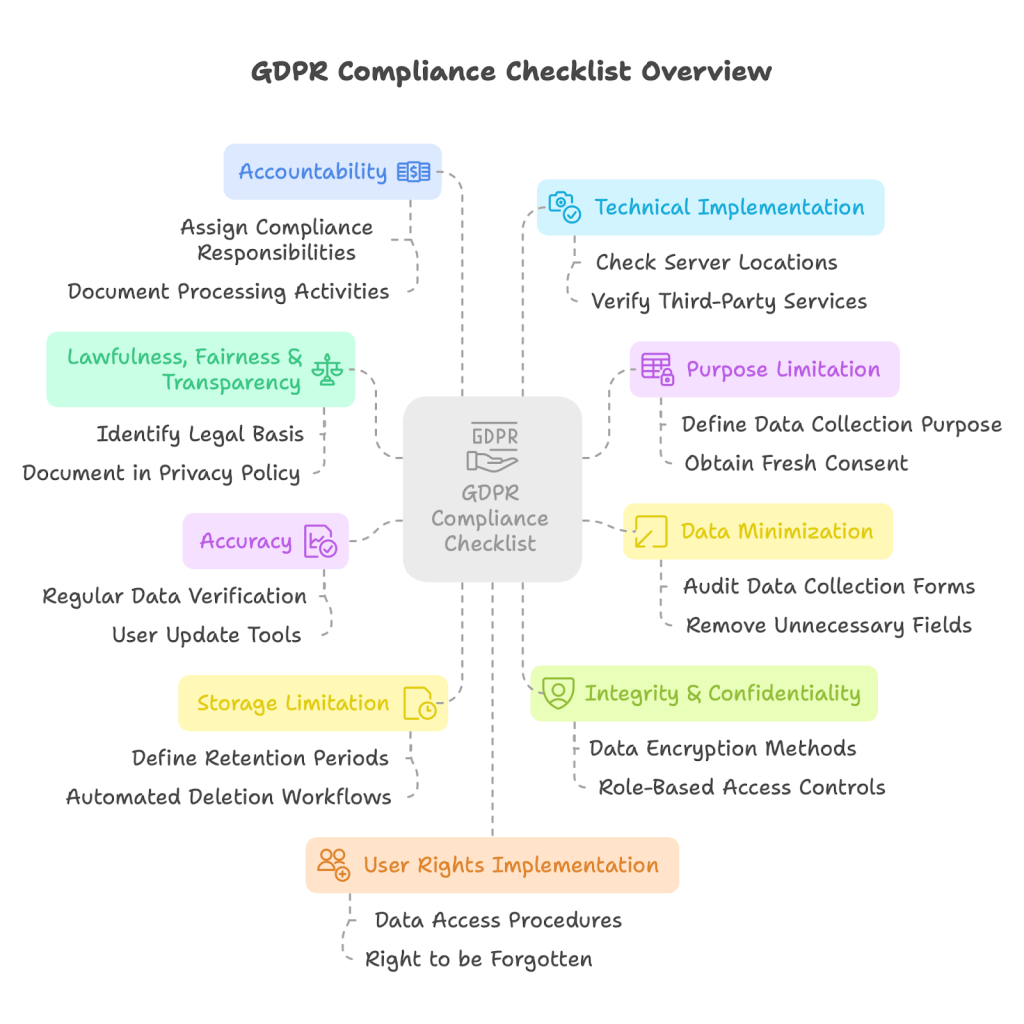
1. Start With a Data Mapping Exercise
Before making changes, understand your current state:
- Identify all personal data collected by your website
- Map where data is stored and who has access
- Document all third-party services receiving data
- Use tools like Violating GDPR to identify data transfers outside the EU
2. Prioritize High-Risk Areas
Some compliance issues are more urgent than others:
- Address any unconsented data transfers outside the EU
- Fix cookie consent mechanisms
- Update forms to include proper consent options
- Review and revise your privacy policy
3. Implement Technical Solutions
Based on your audit findings, make the necessary technical changes:
- Update your cookie management system
- Revise third-party integrations
- Modify forms and data collection points
- Implement mechanisms for exercising user rights
4. Document Your Compliance Efforts
Keep comprehensive records of your compliance measures:
- Maintain a record of processing activities
- Document the legal basis for each type of data processing
- Keep records of consent
- Log changes made to your website for compliance purposes
5. Create an Ongoing Maintenance Plan
Develop procedures to maintain compliance over time:
- Assign responsibility for privacy oversight
- Schedule regular compliance reviews
- Create processes for handling data subject requests
- Establish breach notification procedures
Common GDPR Compliance Mistakes to Avoid
Even with the best intentions, organizations often make these common mistakes:
1. Relying on Cookie Banners Alone
Many websites implement cookie banners that allow users to “accept all” but make it difficult to reject tracking. This doesn’t meet GDPR requirements for freely given consent.
Solution: Implement balanced cookie consent options with equal prominence for “accept” and “reject” buttons.
2. Assuming Compliance Tools Handle Everything
No plugin or tool can guarantee complete GDPR compliance, as compliance involves organizational practices beyond technical implementations.
Solution: Use compliance tools as part of a broader strategy that includes policy development, staff training, and regular audits.
3. Overlooking Data Transfers Outside the EU
Many websites inadvertently transfer personal data outside the EU through CDNs, fonts, analytics, or social media integrations.
Solution: Use tools like the Violating GDPR checker to identify and address these transfers, particularly after the invalidation of Privacy Shield.
4. Collecting Excessive Data “Just in Case”
Gathering more personal data than necessary violates the principle of data minimization.
Solution: Regularly review data collection practices and remove any fields that aren’t essential for your stated purposes.
5. Treating GDPR as a One-Time Project
Privacy regulations and their interpretations evolve, requiring ongoing attention.
Solution: Establish a schedule for regular compliance reviews and updates to your website.
Conclusion: GDPR Compliance as a Competitive Advantage
While achieving GDPR compliance requires effort, it offers significant benefits beyond legal protection:
- Enhanced user trust: Demonstrating respect for privacy builds stronger relationships with your audience
- Improved data practices: The focus on data minimization and purpose limitation leads to cleaner, more valuable data
- Competitive differentiation: Privacy-friendly practices can become a selling point, especially for privacy-conscious consumers
By implementing the changes outlined in this guide, you’re not just avoiding potential penalties—you’re positioning your website as respectful of user privacy in an era where data protection matters more than ever.
Remember, GDPR compliance is a journey, not a destination. Start with the most critical changes, use tools like Violating GDPR to check your current compliance status, and gradually build a comprehensive privacy program that evolves with regulatory changes and user expectations.
Your users will appreciate the transparency and control you provide over their personal data—and that appreciation translates into trust, which remains the foundation of any successful digital relationship.
