GDPR Compliance Checklist for Website Owners (Step-by-Step Guide)
Ensure your website meets GDPR standards with this comprehensive, step-by-step compliance checklist tailored for website owners.
In today’s digital landscape, data privacy isn’t just a nice-to-have—it’s a legal requirement. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has fundamentally changed how websites collect, process, and store personal data.
For website owners, navigating GDPR compliance can seem overwhelming, but the consequences of non-compliance—including hefty fines of up to €20 million or 4% of global annual revenue—make it essential.
This step-by-step checklist will guide you through the process of making your website GDPR compliant, helping you protect your users’ data and your business.
Understanding GDPR Basics
Before diving into technical implementations, it’s important to understand what GDPR is and why it matters to your website.
What is GDPR and Who Does It Apply To?
GDPR is a comprehensive data protection law that came into effect on May 25, 2018. It applies to:
- Organizations established in the EU, regardless of where data processing takes place
- Organizations outside the EU that offer goods or services to EU residents
- Organizations that monitor the behavior of EU residents
Simply put, if you have website visitors from the EU, GDPR likely applies to you, regardless of where your business is located.
Key Principles of GDPR
GDPR is built on seven fundamental principles:
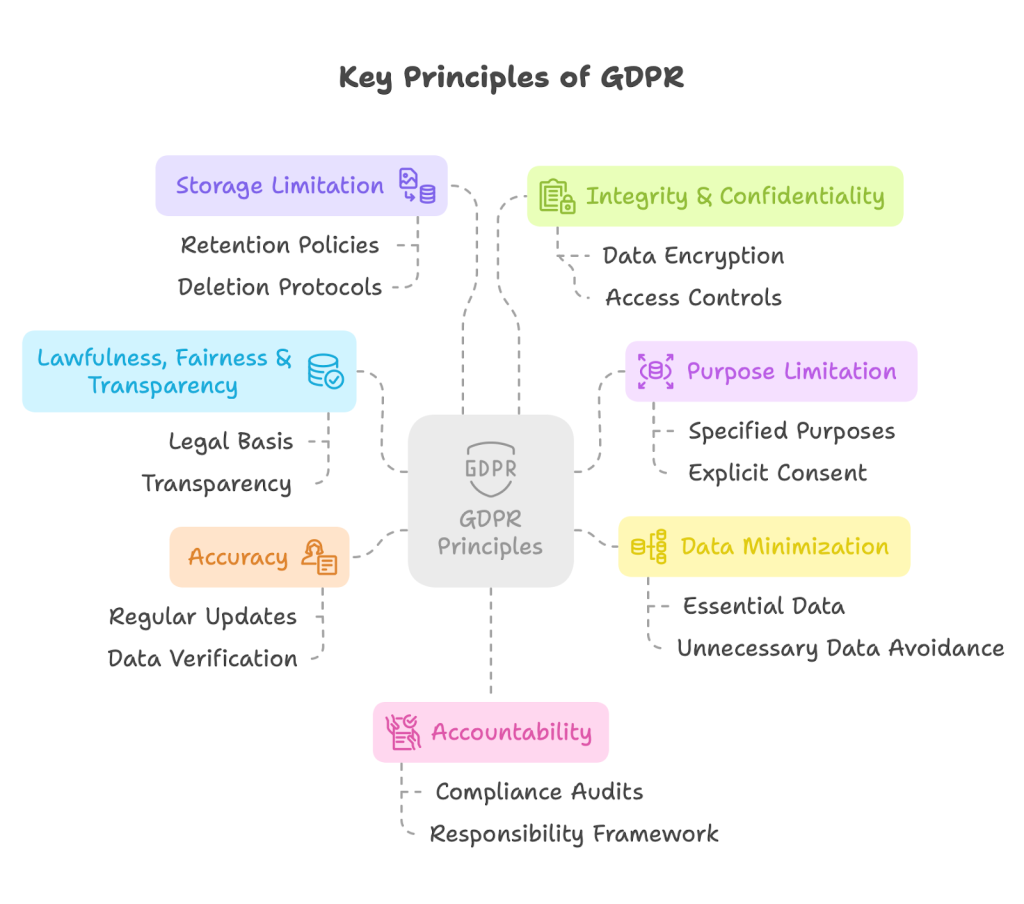
- Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency: Processing must be legal, fair, and transparent to the data subject
- Purpose limitation: You must process data for the legitimate purposes specified to the data subject when you collected it
- Data minimization: You should collect and process only as much data as absolutely necessary
- Accuracy: You must keep personal data accurate and up to date
- Storage limitation: You may only store personally identifying data for as long as necessary
- Integrity and confidentiality: Processing must ensure appropriate security, integrity, and confidentiality
- Accountability: The data controller is responsible for being able to demonstrate GDPR compliance
Recent Court Rulings Affecting Website Owners
Recent court decisions have further clarified GDPR requirements, particularly regarding data transfers outside the EU:
- A German court ruled that embedding Google Fonts directly from Google’s servers violates GDPR because it transfers visitors’ IP addresses to Google’s US-based servers without proper consent (source)
- An Austrian court found that using Google Analytics violates GDPR due to the transfer of personal data to the US (source)
- The French data protection authority ruled that using US-based tools to measure website traffic can breach GDPR (source)
These rulings highlight the growing scrutiny of cross-border data transfers and the need for website owners to be vigilant about where their users’ data goes.
Website Data Audit
Before making changes, you need to understand what personal data your website currently collects and processes.
Identifying Personal Data Collection Points
Conduct a thorough audit of your website to identify all places where you collect personal data:
- Contact forms
- Newsletter sign-ups
- Account registrations
- Comment sections
- E-commerce checkout processes
- Analytics tools
- Social media plugins
- Live chat functionality
- Feedback or survey forms
- Embedded third-party content
Mapping Data Flows
For each data collection point, document:
- What specific data is collected (name, email, IP address, etc.)
- Why it’s collected (purpose)
- How long it’s stored
- Who has access to it (including third-party services)
- Where it’s physically stored (which servers, in which countries)
Identifying Third-Party Services
Many websites use third-party services that may transfer data outside the EU. Common examples include:
- Google Analytics
- Google Fonts
- Facebook Pixel
- Google Maps
- YouTube embeds
- Social media sharing buttons
- Third-party advertising networks
- Customer relationship management tools
- Email marketing platforms
- Content delivery networks (CDNs)
A quick way to check if your website might be transferring data outside the EU is to use our free tool at Violating GDPR. This tool scans your website for embedded third-party content that might send visitors’ IP addresses to non-EU servers.
Essential Website Modifications
Now that you understand what personal data you’re collecting, it’s time to implement necessary changes to your website.
Privacy Policy Requirements
Your privacy policy must be:
- Written in clear, plain language
- Easily accessible
- Comprehensive about your data practices
Your privacy policy should include:
- Your identity and contact information
- Types of data collected
- Purpose of processing
- Legal basis for processing
- Data retention periods
- Third parties with whom data is shared
- Information about international transfers
- Security measures in place
- Data subject rights
- Right to withdraw consent
- Right to lodge a complaint with a supervisory authority
- Whether providing personal data is mandatory and the consequences of not providing it
- Information about automated decision-making, including profiling
Cookie Consent Banners
Under GDPR, you need explicit consent before setting non-essential cookies. Your cookie consent banner should:
- Be visible and clear
- Explain what cookies are used and why
- Allow users to selectively accept or reject different categories of cookies
- Not pre-tick optional cookie categories
- Be as easy to withdraw consent as it is to give it
- Work correctly (many cookie banners are incorrectly implemented and still set cookies even when users reject them)
Critically, you cannot deny access to your website if someone refuses non-essential cookies.
Form Modifications
For any forms collecting personal data:
- Include clear explanations of why you’re collecting each piece of information
- Only collect necessary information (data minimization)
- Add checkboxes for consent that aren’t pre-selected
- Separate essential and non-essential data collection
- Provide links to your privacy policy
Data Subject Rights Implementation
Ensure you have processes in place to handle these data subject rights:
- Right to access their personal data
- Right to rectification of inaccurate data
- Right to erasure (the “right to be forgotten”)
- Right to restrict processing
- Right to data portability
- Right to object to processing
- Rights related to automated decision making and profiling
This typically means having clear contact information for data requests and internal procedures for handling these requests within the required timeframe (usually 30 days).
Technical Implementation Steps
Now let’s look at specific technical changes you may need to make to your website.
Server Location Considerations
While not explicitly required by GDPR, using EU-based servers can simplify compliance by keeping personal data within the EU. Consider:
- Where your web hosting servers are located
- Where your database servers are located
- Where your backup data is stored
Self-Hosting Critical Resources
As highlighted by the German court ruling on Google Fonts, loading resources directly from third-party servers can transfer users’ IP addresses outside the EU. Consider self-hosting:
- Fonts (instead of loading from Google Fonts)
- JavaScript libraries (instead of loading from CDNs)
- Images and videos
- CSS files
For WordPress sites, plugins like OMGF (Optimize My Google Fonts) can help you easily self-host Google Fonts.
Analytics Solutions
Standard Google Analytics has been ruled non-compliant by several EU authorities. Consider:
- Server-side analytics that doesn’t share data with third parties
- EU-based analytics platforms (like Matomo hosted in the EU)
- Privacy-focused analytics (like Fathom or Plausible)
- Using IP anonymization if you must use Google Analytics
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
CDNs can improve website performance but may transfer data outside the EU. Options include:
- Using EU-only CDN endpoints
- Working with CDN providers that offer GDPR-compliant solutions
- Implementing proper data processing agreements with your CDN provider
Website Auditing Tools
Regular technical audits can help ensure ongoing compliance. Our free tool at Violating GDPR offers a quick initial check of your website to see if it’s transferring data outside the EU through embedded resources like scripts, iframes, images, or videos.
While this is just a starting point, it can help identify obvious compliance issues that need addressing. For a comprehensive compliance check, you might need more detailed tools and potentially legal advice.
Ongoing Compliance Management
GDPR compliance isn’t a one-time project but an ongoing responsibility.
Regular Compliance Reviews
Schedule regular reviews of your website’s GDPR compliance, including:
- Quarterly audits of data collection practices
- Regular checks of third-party services
- Updates to privacy policies when practices change
- Testing of data subject rights procedures
Staff Training
Ensure that everyone involved in your website understands:
- Basic GDPR principles
- Your specific data handling procedures
- How to recognize and respond to data subject requests
- The importance of data protection by design
Documentation Requirements
Maintain documentation of your GDPR compliance efforts, including:
- Records of processing activities
- Data protection impact assessments (for high-risk processing)
- Records of consent
- Data breach procedures and records
- Data processing agreements with third parties
Keeping Up With Regulatory Changes
GDPR interpretation continues to evolve through court decisions, regulatory guidance, and new legislation. Stay informed through:
- Subscribing to privacy law updates
- Following relevant data protection authorities
- Joining industry groups focused on data protection
- Regular consultations with privacy professionals
Practical Implementation Example
Let’s look at a practical example of implementing GDPR compliance for a typical business website:
Case Study: A Small Business Website
A small business website collects visitor data through a contact form, uses Google Analytics for visitor tracking, embeds YouTube videos, uses Google Fonts, and has a newsletter signup form.
Step 1: Data Audit
They identified all personal data collection points and documented the purpose for each.
Step 2: Privacy Policy Update
They created a comprehensive privacy policy explaining all data collection and processing.
Step 3: Cookie Consent Implementation
They implemented a GDPR-compliant cookie banner that:
- Explained all cookies used
- Grouped cookies by purpose (necessary, analytics, marketing)
- Allowed selective acceptance
- Stored consent for their records
Step 4: Technical Changes
- They self-hosted Google Fonts instead of loading them from Google’s servers
- Switched to Plausible Analytics (EU-hosted) instead of Google Analytics
- Used YouTube’s enhanced privacy mode for video embeds
- Added proper consent checkboxes to their contact and newsletter forms
Step 5: Documentation
They created internal documents detailing their compliance measures and staff training.
Step 6: Ongoing Management
They scheduled quarterly compliance reviews and assigned a team member to stay updated on GDPR developments.
Verification
After implementing these changes, they used the Violating GDPR tool to verify they were no longer sending data outside the EU unnecessarily.
Conclusion
While GDPR compliance may seem daunting, breaking it down into manageable steps makes it achievable for website owners of all sizes. The key is to start the process now rather than waiting for a complaint or investigation.
Remember that GDPR compliance isn’t just about avoiding fines—it’s about respecting user privacy and building trust with your audience. Websites that demonstrate a commitment to data protection often see improved user trust and engagement.
Start your compliance journey today with a simple first step: use our free tool at Violating GDPR to check if your website is sending data outside the EU. This quick check can identify immediate issues to address while you work through the more comprehensive checklist provided in this guide.
By following this step-by-step approach, you’ll not only work toward GDPR compliance but also demonstrate to your users that you value and protect their privacy—something increasingly important in today’s digital world.
Remember, while this guide provides a solid starting point, complex websites or unique data processing activities may require additional measures and potentially legal advice to ensure full compliance.
